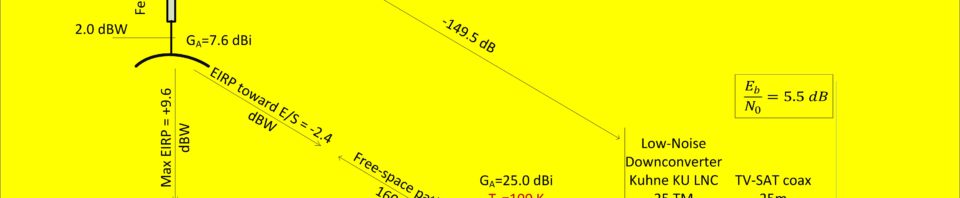
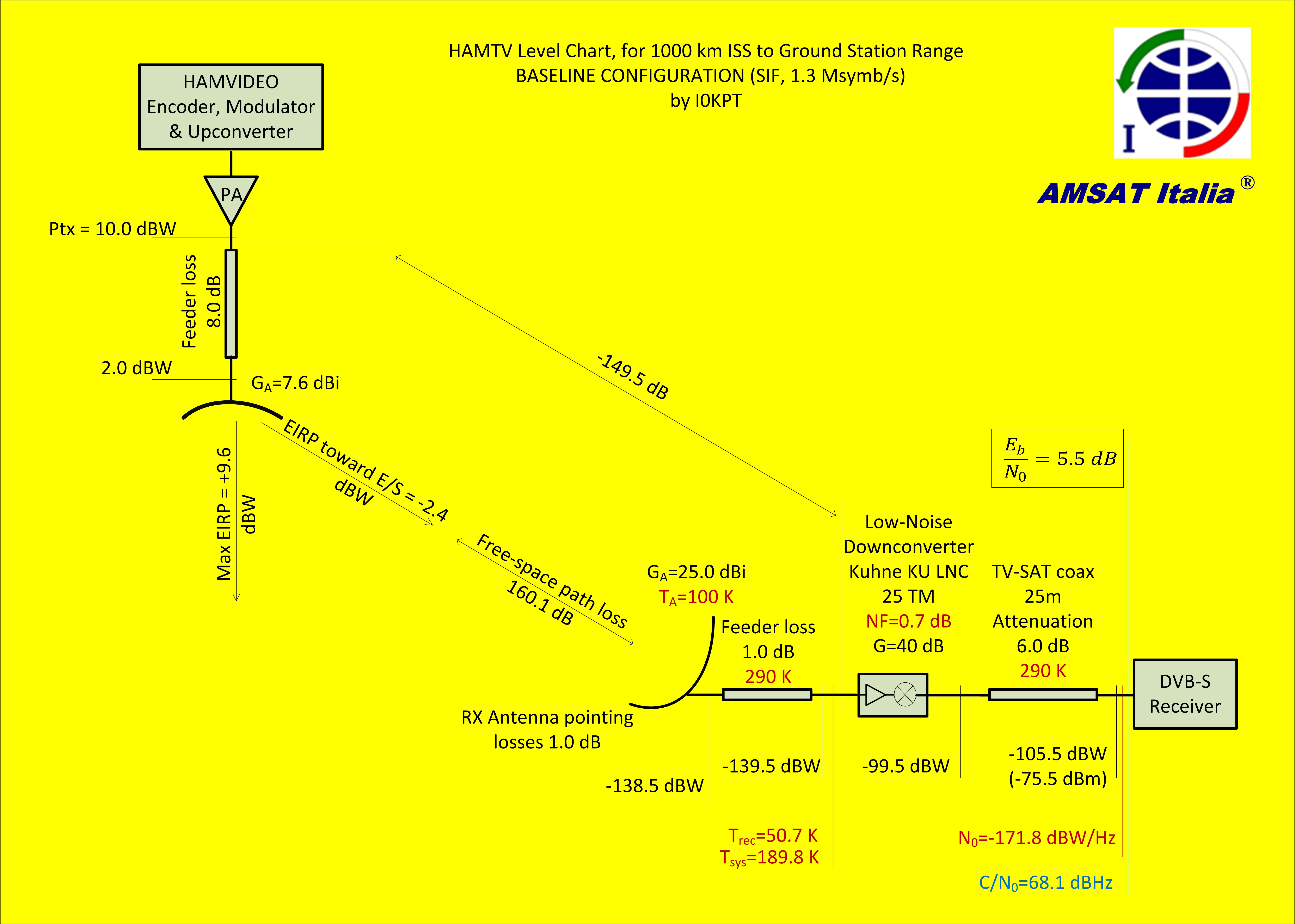
The HamVideo power levels in the table at the bottom of this page result from worst case computations, intended for the evaluation of system efficiency. See Link budget computation by I0KPT.
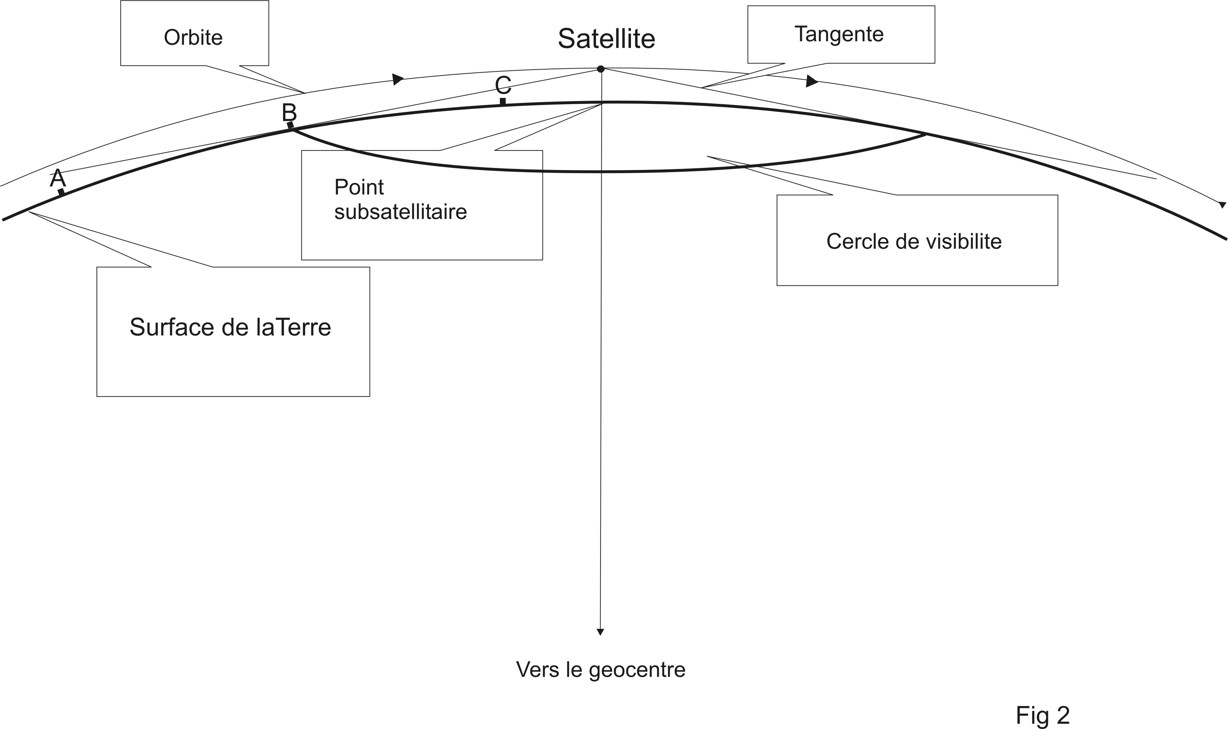
As shown in fig 2, the ISS orbits at about 400km above the surface of the earth. That is the distance between the ISS and the « subsatellite point ».
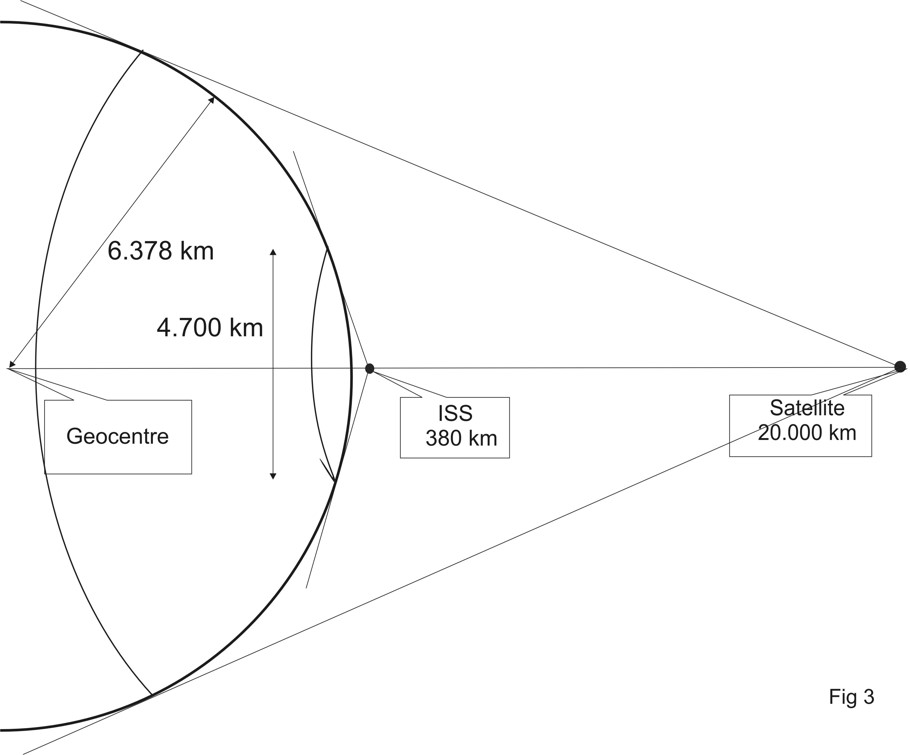
The tangent from the ISS to the surface of the earth (Fig 2, point B) describes a « circle of visibility » with a diameter of about 4700km (see fig 3). At places on the earth at a distance of 2350km from the SSP, the ISS rises over the horizon at the start of a pass and disappears over the horizon at the end of the pass. For these locations and at that moment, the elevation angle versus the horizon is zero degree and the « slant range » (= straight line distance to the satellite) is maximum.
At the middle of the pass, the elevation angle is maximum and the slant range is minimum. For an overhead pass of the ISS, the elevation is then 90 degrees and the slant range 400km.
In theory, VHF communication with the ISS is possible as soon as the location of the ground station is within the circle of visbility. At that moment, the radio waves travel a considerable distance through low atmosphere, highly affected by manmade radioelectrical pollution. Absorption of radiated power and noise interference is maximum. Solid VHF communication becomes possible when the ISS is about 5-10 degrees above the horizon. The slant range is then about 2000km.
For HamVideo reception, the slant range should not exceed 1000km. This corresponds to a « circle of HamVideo reception » with a diameter of about 800km.
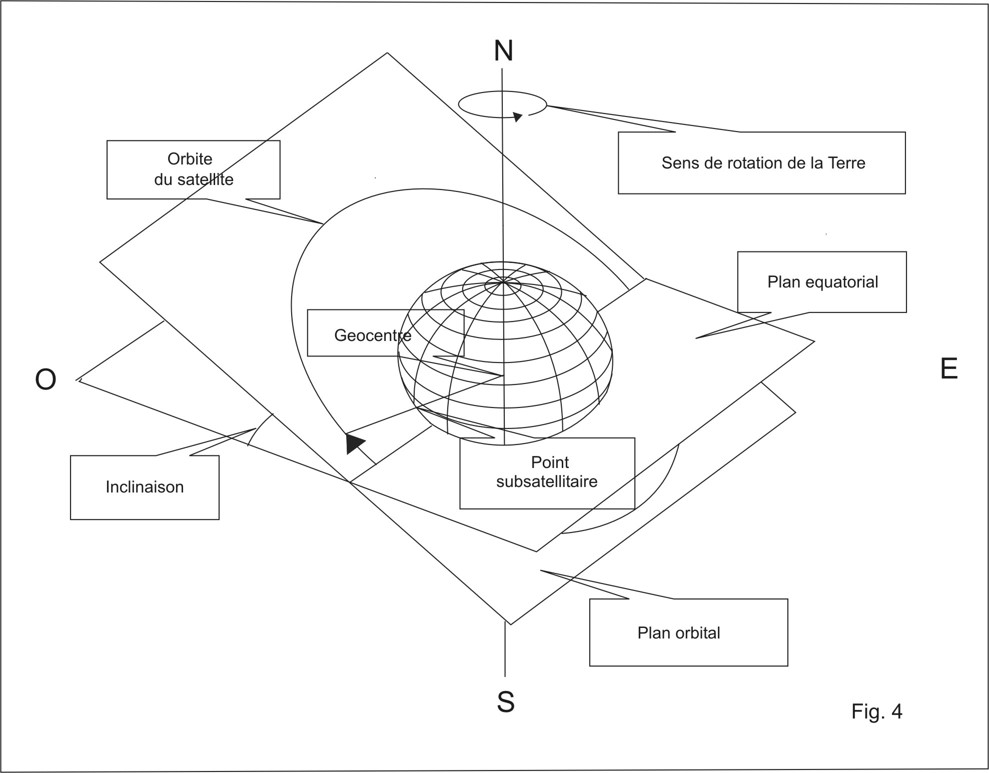
Remark: the orbital plane of the ISS has an inclination of 51 degrees versus the equator. See fig 4.
| Element | Power per element
(loss = negativ) |
Total Power | Remarks |
| Ham TV PA output | 10.0 dBW | 10.0 dBW | Transmitter output power measured with spectrum analyser – equivalent thermal power |
| Feeder loss | -8.0 dB | 2.0 dBW | |
| Antenna gain in direction of maximum antenna gain | 7.6 dBi | 9.6 dbW | EIRP toward sub satellite point (SSP) |
| Antenna gain toward location 800km from SSP | -4.4 dBi | -2.4 dBW | EIRP for 1000km slant range |
| Free space loss | -160.1 dB | -162.5dBW | Loss for 1000km slant range |
| Receiving antenna gain | 25 0 dBi | -137.5 dBW | |
| Receiving antenna pointing loss | -1.0 dB | -138.5 dBW | |
| Feeder loss | -1.0 dB | -139.5 dBW | |
| Downconverter gain | 40 dB | -99.5 dBW | |
| Coaxial cable loss (25m cable) | – 6 dB | -105.5 dBW | -75.5 dBm presented to receiver input |